Correlation matrix : A quick start guide to analyze, format and visualize a correlation matrix using R software
What is correlation matrix
Correlation matrix or covariance matrix is used to investigate the dependence between multiple variables at the same time. The result is a table containing the coefficients of correlation between each variable and the others. There are different methods for correlation analysis : Pearson correlation test, Spearman and Kendall rank-based correlation analysis. These methods are discussed in the next sections. Correlation matrix can be visualized using correlogram. The aim of this article is to show you how to compute and visualize a correlation matrix in R.
Correlation analysis in R
The R function cor() can be used to compute a correlation matrix. A simplified format of the function is :
# x is a matrix or data.frame
cor(x, method = c("pearson", "kendall", "spearman"))The argument method= indicates the correlation coefficient to be computed. The default is pearson correlation coefficient which measures the linear dependence between two variables. kendall and spearman correlation methods are non-parametric rank-based correlation test.
data for correlation analysis
The mtcars data is used in the following examples to compute the correlation matrix.
head(mtcars) mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am gear carb
Mazda RX4 21.0 6 160 110 3.90 2.620 16.46 0 1 4 4
Mazda RX4 Wag 21.0 6 160 110 3.90 2.875 17.02 0 1 4 4
Datsun 710 22.8 4 108 93 3.85 2.320 18.61 1 1 4 1
Hornet 4 Drive 21.4 6 258 110 3.08 3.215 19.44 1 0 3 1
Hornet Sportabout 18.7 8 360 175 3.15 3.440 17.02 0 0 3 2
Valiant 18.1 6 225 105 2.76 3.460 20.22 1 0 3 1Correlation matrix
mcor <- cor(mtcars)
mcor mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec vs am gear carb
mpg 1.00 -0.85 -0.85 -0.78 0.68 -0.87 0.42 0.66 0.60 0.48 -0.55
cyl -0.85 1.00 0.90 0.83 -0.70 0.78 -0.59 -0.81 -0.52 -0.49 0.53
disp -0.85 0.90 1.00 0.79 -0.71 0.89 -0.43 -0.71 -0.59 -0.56 0.39
hp -0.78 0.83 0.79 1.00 -0.45 0.66 -0.71 -0.72 -0.24 -0.13 0.75
drat 0.68 -0.70 -0.71 -0.45 1.00 -0.71 0.09 0.44 0.71 0.70 -0.09
wt -0.87 0.78 0.89 0.66 -0.71 1.00 -0.17 -0.55 -0.69 -0.58 0.43
qsec 0.42 -0.59 -0.43 -0.71 0.09 -0.17 1.00 0.74 -0.23 -0.21 -0.66
vs 0.66 -0.81 -0.71 -0.72 0.44 -0.55 0.74 1.00 0.17 0.21 -0.57
am 0.60 -0.52 -0.59 -0.24 0.71 -0.69 -0.23 0.17 1.00 0.79 0.06
gear 0.48 -0.49 -0.56 -0.13 0.70 -0.58 -0.21 0.21 0.79 1.00 0.27
carb -0.55 0.53 0.39 0.75 -0.09 0.43 -0.66 -0.57 0.06 0.27 1.00In the table above correlations coefficients between the possible pairs of variables are shown.
If your data contain missing values, use the following R code to handle missing values by case-wise deletion.
cor(mtcars, use = "complete.obs")Correlation significance levels (p-value)
The output of cor() function is the correlation coefficients between each variable and the others. However the function doesn’t display the correlation signicance levels (p-value). In the next section, we will use Hmisc R package to calculate correlation p-value.
The function rcorr() from Hmisc package can be used to compute the significance levels for pearson and spearman correlations. Using this function, Pearson’s r or Spearman’s rho rank correlation coefficients are computed for all possible pairs of columns in the data table.
The simplified format is :
rcorr(x, type=c("pearson","spearman"))x should be a matrix. The correlation type can be pearson or spearman.
library(Hmisc)
rcorr(as.matrix(mtcars[,1:7])) mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec
mpg 1.00 -0.85 -0.85 -0.78 0.68 -0.87 0.42
cyl -0.85 1.00 0.90 0.83 -0.70 0.78 -0.59
disp -0.85 0.90 1.00 0.79 -0.71 0.89 -0.43
hp -0.78 0.83 0.79 1.00 -0.45 0.66 -0.71
drat 0.68 -0.70 -0.71 -0.45 1.00 -0.71 0.09
wt -0.87 0.78 0.89 0.66 -0.71 1.00 -0.17
qsec 0.42 -0.59 -0.43 -0.71 0.09 -0.17 1.00
n= 32
P
mpg cyl disp hp drat wt qsec
mpg 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0171
cyl 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0004
disp 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0131
hp 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0100 0.0000 0.0000
drat 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0100 0.0000 0.6196
wt 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.0000 0.3389
qsec 0.0171 0.0004 0.0131 0.0000 0.6196 0.3389 As an output, the rcorr() function returns a list with elements : - r : the matrix of correlations - n : the matrix of number of observations used in analyzing each pair of variables - P : the p-values corresponding to the significance levels of correlations.
Correlogram : Visualization of correlation matrix
Several methods are available to plot a correlogram in R. You can use either R symnum function, corrplot function or scatter graph to make a graph of correlation matrix.
Use symnum function
The R function symnum replaces correlation coefficients by symbols according to the value. It takes the correlation matrix as an argument :
symnum(mcor) m cy ds h dr w q v a g cr
mpg 1
cyl + 1
disp + + 1
hp , + , 1
drat , , , . 1
wt + , + , , 1
qsec . . . , 1
vs , + , , . . , 1
am . . . , , 1
gear . . . , . , 1
carb . . . , . , . 1
attr(,"legend")
[1] 0 ' ' 0.3 '.' 0.6 ',' 0.8 '+' 0.9 '*' 0.95 'B' 1As indicated in the legend, the correlation coefficients between 0 and 0.3 are replaced by a space (" “); correlation coefficients between 0.3 and 0.6 are replace by”.“; etc …
Correlogram using R corrplot function
You have to install corrplot package which performs a graphical display of a correlation matrix in R.
To read more about corplot() function click here : visualize a correlation matrix using corrplot.
The function corrplot takes the correlation matrix as the first argument. The second argument (type=“upper”) is used to display only the upper triangular of the correlation matrix.
library(corrplot)
corrplot(mcor, type="upper", order="hclust", tl.col="black", tl.srt=45)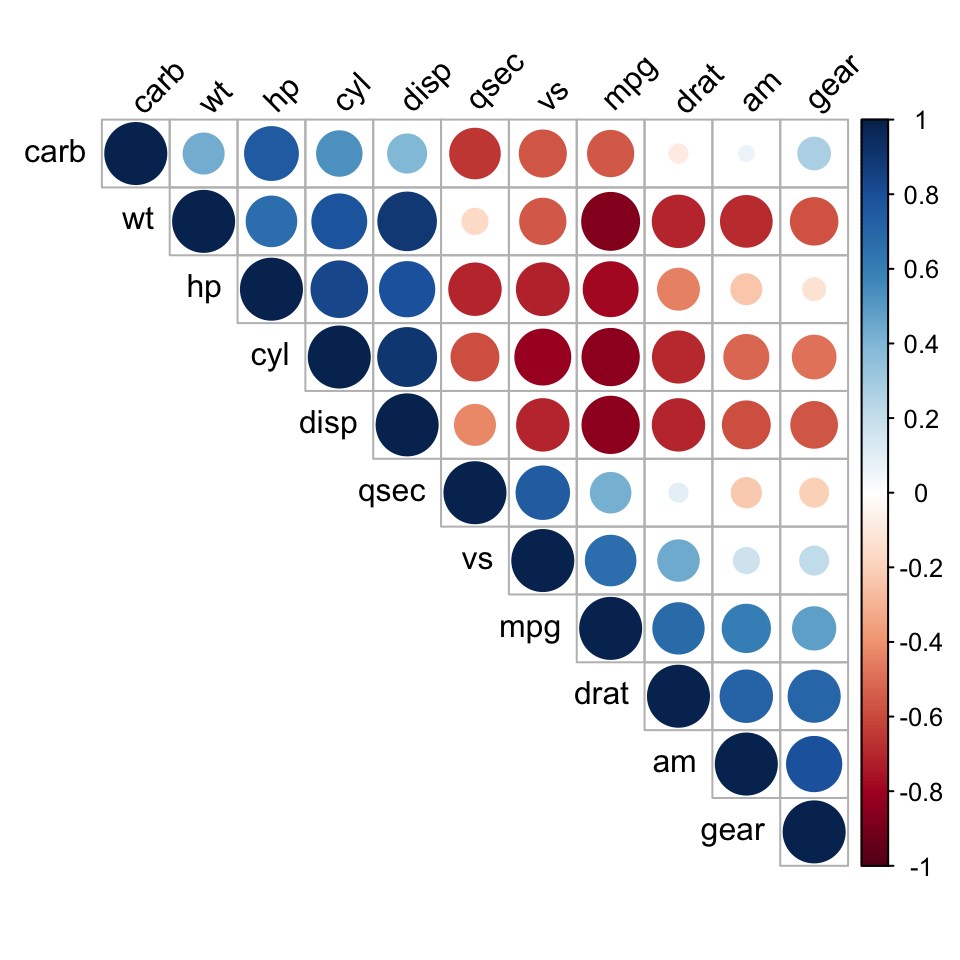
Positive correlations are displayed in blue and negative correlations in red color. Color intensity and the size of the circle are proportional to the correlation coefficients. In the right side of the correlogram, the legend color shows the correlation coefficients and the corresponding colors.
The correlation matrix is reordered according to the correlation coefficient using “hclust” method. tl.col (for text label color) and tl.srt (for text label string rotation) are used to change text colors and rotations.
conclusinons
- Use cor() function for simple correlation analysis
- Use rcorr() function from Hmisc package to compute matrix of correlation coefficient and matrix of p-value in single step.
- Use symnum() function or corplot() function [from corrplot package] to make a graph of a correlation matrix
Infos
This analysis was performed using R (ver. 3.1.0).Show me some love with the like buttons below... Thank you and please don't forget to share and comment below!!
Montrez-moi un peu d'amour avec les like ci-dessous ... Merci et n'oubliez pas, s'il vous plaît, de partager et de commenter ci-dessous!
Recommended for You!
Recommended for you
This section contains the best data science and self-development resources to help you on your path.
Books - Data Science
Our Books
- Practical Guide to Cluster Analysis in R by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
- Practical Guide To Principal Component Methods in R by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
- Machine Learning Essentials: Practical Guide in R by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
- R Graphics Essentials for Great Data Visualization by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
- GGPlot2 Essentials for Great Data Visualization in R by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
- Network Analysis and Visualization in R by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
- Practical Statistics in R for Comparing Groups: Numerical Variables by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
- Inter-Rater Reliability Essentials: Practical Guide in R by A. Kassambara (Datanovia)
Others
- R for Data Science: Import, Tidy, Transform, Visualize, and Model Data by Hadley Wickham & Garrett Grolemund
- Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras, and TensorFlow: Concepts, Tools, and Techniques to Build Intelligent Systems by Aurelien Géron
- Practical Statistics for Data Scientists: 50 Essential Concepts by Peter Bruce & Andrew Bruce
- Hands-On Programming with R: Write Your Own Functions And Simulations by Garrett Grolemund & Hadley Wickham
- An Introduction to Statistical Learning: with Applications in R by Gareth James et al.
- Deep Learning with R by François Chollet & J.J. Allaire
- Deep Learning with Python by François Chollet
Click to follow us on Facebook :
Comment this article by clicking on "Discussion" button (top-right position of this page)







